Dualstack Routing¶
UH VPN is capable of handling both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic and has built in support for dualstack VPN tunneling.
In order to enable dualstack operation it is imperative that the following prerequisites are met:
IPv6 Public Subnet Issued: You must have an IPv6 public subnet issued to you by a relevant Internet registry applicable to your geographical area. E.g. RIPE, ARIN and so on. From this subnet you must choose a /64 subnet as the IPv6 tunnel network.
IPv6 Routing: The entire IPv6 /64 subnet used as the IPv6 tunnel network must be routed to your VPN server. For example, if your VPN server has the public facing IPv6 address of
2000::1/32and you plan to use the subnet of2000:0000:0000:0001::/64as your tunnel network, you must have a route marking2000::1/32as the next hop address for the subnet2000:0000:0000:0001::/64at your upstream router to avoid NDP failures. Without this routing rule in place, IPv6 traffic will not reach connecting clients.
Once these two prerequisites are met, it’s simple to enable dualstack support on a UH VPN server.
First head over to the website and within the appropriate group, edit the relevant server and include your public IPv6 subnet in the “IPv6 Tunnel Network” field as indicated below:
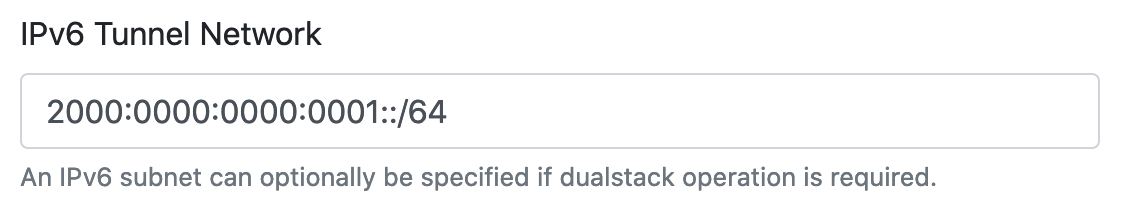
Once entered, save the server configuration. Future connecting clients will then be issued an IPv6 address from the /64 network specified above and enjoy dualstack connectivity to the Internet.